If CPI Measured Actual House Prices, Inflation Would Be 3% Right Now
Tyler Durden
Sun, 11/29/2020 – 17:00
Submitted by Joseph Carson, formerly chief economist at AllianceBernstein
“Actual” consumer price inflation is rising during the recession. That runs counter to the normal recessionary pattern when the combination of weak demand and excess capacity works to lessen inflationary pressures.
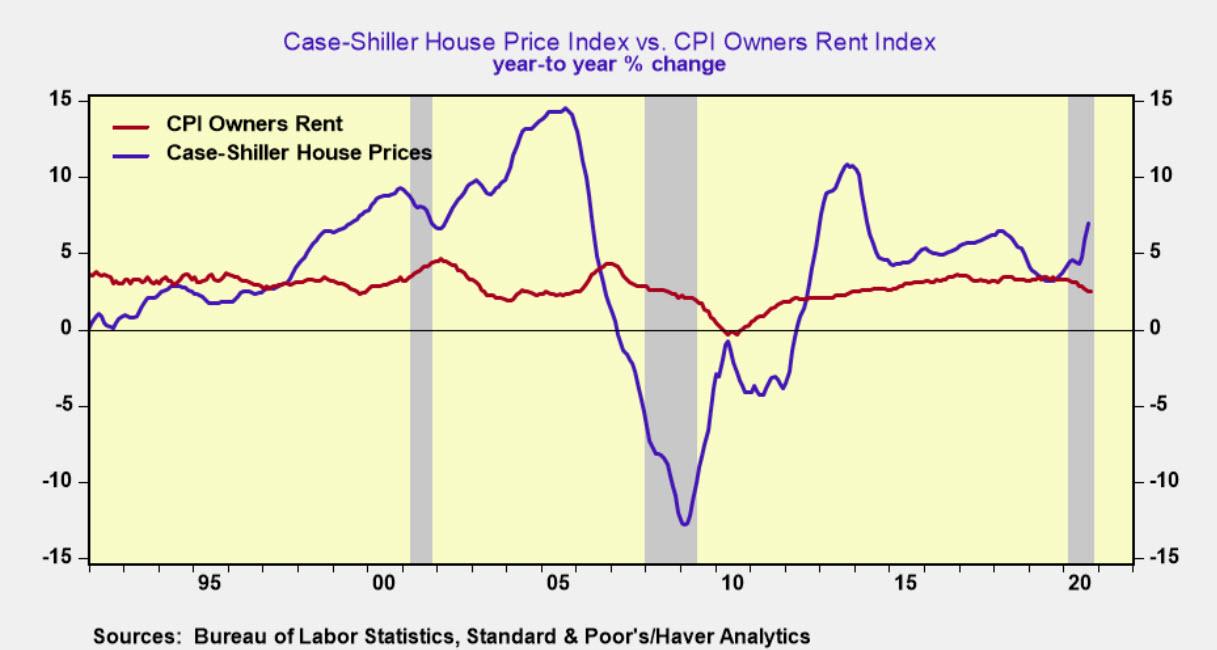
The main source of faster consumer price inflation is centered in the housing market. The Case-Shiller Home Price Index posted a 7% increase the last year, more than twice the gain of one-year ago.
The sharp acceleration in house price inflation represents the fastest increase since 2014 and runs counter to the patterns of the past two recessions. During the 2001 recession house price inflation slowed by one-third, while in the Great Financial Recession housing prices posted their largest decline in the post-war period, falling over 12% nationwide.
The consumer price index (CPI) does not show in house price inflation because it uses a non-market rent index to capture the trends in housing inflation. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) estimates that the non-market rent index has increased 2.5% in the past 12 months, or 450 basis points below the rise in house prices.
If actual house prices were used in place of rents core CPI would have registered a 3% gain in the past year, nearly twice the reported gain of 1.6%.
If aggregate price measures did not exist house prices would be one of the most important measures to gauge inflation and the proper setting of official interest rates. That’s because house price cycles include easy credit/financial conditions, excess demand, and inflation expectations, three key ingredients of inflation cycles.
Rising consumer price inflation is added to the list of unique features of the 2020 recession. Others include an increase in corporate debt levels instead of debt-liquidation and rising equity prices instead of share price declines.
If the 2020 recession has economic and financial features that normally appear during economic recovery what does that imply for the next growth cycle? The debt overhang at the corporate and federal debt should impede the next growth cycle. And if the cyclical rise in housing demand is occurring in recession it can’t be repeated during recovery.
The next economic cycle will be filled with unique tipping points, and no one should assume that policymakers can control or offset them.